F14
Contents
DCS F-14 A/A introductory Guide
Introduction
The F14 is a heavy US naval fighter designed for the intercept role but can act as an air superiority fighter engaging enemy fighters.
- Weapons
- AIM54
- AIM7
- AIM9
- Pilot Seat
- Keybinds
- Viewing the radar
- HUD/ACM - important elements
Weapons
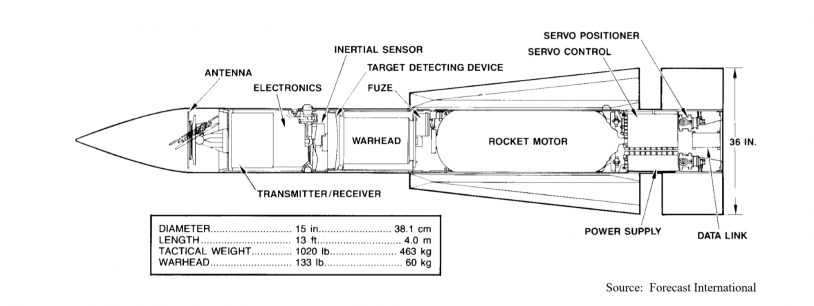
AIM-54
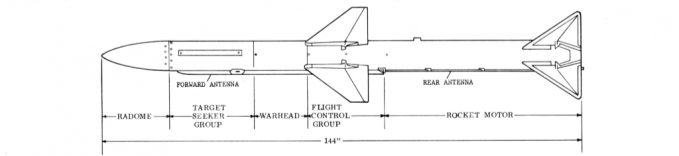
The AIM-54 will be the most used A/A weapon for the F14 and is unique to this aircraft. It is a long range actively guided A/A missile. It was originally meant to be deployed on the F111B to intercept bombers and cruise missiles at very long range. Additionally, learning from the Vietnam conflict, the missile also had to be able to engage maneuverable fighter aircraft at medium ranges with high hit rates. This led to a missile which in testing achieved a max range shot of ~115nm and was the first missile to hit a target pulling more than 6g's successfully.
(note this next part is WIP as of 7/14/2019 as we are waiting for HB to get access to a working missile API but once they do the AIM-54 will behave as described in the following text. Until then it acts essentially like an AMRAAM)
Due to the more antiquated nature of its electronics the 54 does have downsides to its deployment. First, it is not truly fire and forget in TWS mode like the AMRAAM is. The computer has to tell the missile to go active via a RF pulse sent through the missiles datalink. This is often commanded 16sec before impact. Tactically speaking this means a turn too far away from the target will result in the missile not receiving the pitbull command. This can be averted if the pilot flips up the ACM cover (missile is active off the rail) or if the RIO manually gives the command via a switch in the back.
On the other hand when using STT the missile will go into a SARH mode. While operating in SARH mode if the STT lock is lost the missile will not turn on its own radar until the pitbull command is received. However if the STT lock is re-acquired the missile will continue to guide until it goes active. Additionally, while in a Pulse STT lock the missile will not be able to loft and will not receive the range befit this provides.
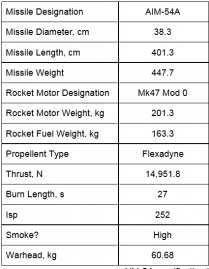
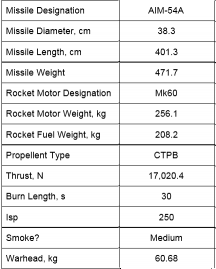
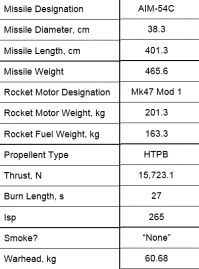
There are 3 main types of AIM-54:
| A-47 | A-60 | C-47 |
*From HB http://media.heatblur.se/AIM-54.pdf
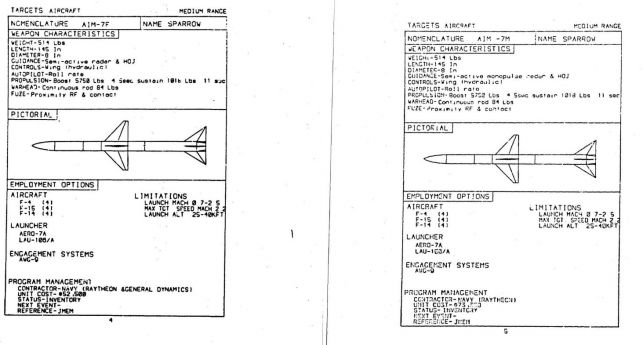
AIM-7
The Sparrow III is the third major revision of the venerable sparrow design of the early 1950's. It was the frontline BVR A/A missile for the United States Airforce, Marine Core, and Navy until the early to mid 1990's; ultimately being replaced by the AIM-120 series of missiles. The sparrow III, when compared to its predecessors, is a significant improvement in every way, it features a design that was easily upgradable over time. The ultimate version we have in DCS the MH variant features lofting logic and improved CCM performance over previous models.
F
The first Sparrow variant fielded of the new type the F sets the aerodynamics and range for all futures sparrows. Unique to this variant is the ability to home in on either a CW signal or a PD signal. Even though not implemented on the F14 yet, in the future you should be able to choose between the two modes. This in game means all three types of sparrow perform kinematically the same, however the F's chaff resistance is extremely low and can be decoyed with only a few chaff bundles.
M
The upgrade to the F-model, the M build irl received a new, and substantially better, monopulse seeker and a chose between two nose cones. One optimized for radar performance the other for aerodynamic performance. The monopulse seeker gives this missiles an inherent resistance to chaff and ECM in addition it can only home in on a PD signal. In game the only difference from the F is a substantially improved chaff resistance.
MH
The MH variant is the most modern sparrow currently in DCS. This variant uses parts from the AIM-7P to improve its long range performance with lofting and low altitude performance with newer guidance computers. Additionally the CCM logic was upgraded substantially. In game this makes the MH the most effective variant due to its lofting and CCM performance making chaff have a low effectiveness against it.
AIM-9
The Sidewinder is the longest serving missile series in the world. It has seen massive improvements over the more than 50 years it has been in serviece. The F14 can currently carry two types the AIM-9L and the AIM-9M.
L
The '9L' was the first of the "unified" Sidewinder models, as previously the Airforce and Navy had their own unique model, this one was the first to be used by both branches. The L was a major upgrade over all previous sidewinders, heavily based on the AIM-9H the ultimate navy only variant. The L featured a new cooled InSb (Indium Antimonide) FM spin seeker which provides some natural resistance to IR counter measures, a completely new electronics package, increased off boresight capabilities, higher max G, higher launch g (7g's), much longer flight time of 1 minute, New warhead, new and more powerful motor.
M
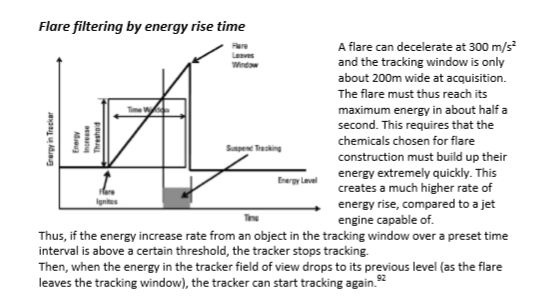
The '9M' in shape, size, weight, and even appearance is the same missle. But on the inside its electronics got complelty oveerhauld. These new electronics could now filter out falres based on a flares energy rise time.
and it also proved for more background noise filtering. In addition to this the 9M got a new smokless motor that
RIO Seat
Controls:
Setup:
Radar Modes:
PD
RWS
TWS Auto
TWS Manual
Pulse
TID
DDD
Pilot Seat
Controls:
Setup:
1) Set Hud to A/A mode
2) ()
3) Master Arm to cover up and switch up.
4) Select Weapon
A/A HUD
Pilot controls over the radar:
PLM
VSL Hi/Low
PAL