Difference between revisions of "M2k"
m (Page updates) |
m |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==DCS M-2000C A/A introductory Guide== | ==DCS M-2000C A/A introductory Guide== | ||
| − | ==Introduction | + | ==Introduction== |
| − | The Mirage-2000C is a light | + | The Mirage-2000C is a light delta wing interceptor built in France. It has a very limited A/A loadout with only 2x R550 Magic II short range IR missiles and 2x Super 530D medium range SARH missiles. The Mirage in terms of systems is very simple and is in general an easy aircraft to learn and operate. This makes it a great first fighter. Even though completely outmatched against western contemporaries such as the F15C and F14A/B in BVR combat this jet at the short to medium ranges can be lethal. In particular against older Russian aircraft such as the MIG-23 this aircraft can be downright lethal. |
*Weapons | *Weapons | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | ==Weapons | + | ==Weapons== |
===Super 530D=== | ===Super 530D=== | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
==Controls== | ==Controls== | ||
| − | === Pilot Stick === | + | ===Pilot Stick=== |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | === Pilot Throttle === | + | ===Pilot Throttle=== |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
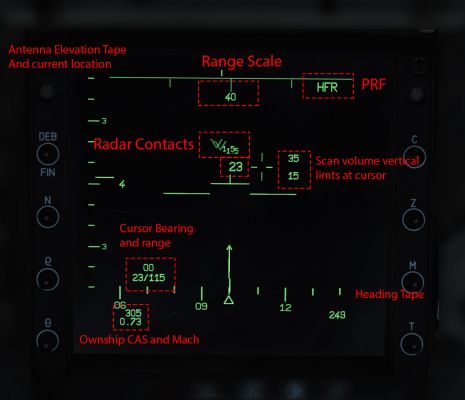
==Radar Page (RWS):== | ==Radar Page (RWS):== | ||
| + | The radar is the heart of the offensive systems in the mirage. The radar scope is the screen situated just below the hud and is dedicated to the radar. The radar has several useful features that make it quite good at helping the pilot better understand the air picture without the assistance of a datalink which the mirage lacks. However the small size of the radar limits its long range detection capabilities especially when compared to other fighters in DCS. | ||
===PPI Scope=== | ===PPI Scope=== | ||
| Line 38: | Line 39: | ||
The PPI scope is a more accurate representation of what your radar is seeing. It displays the radar in a cone like shape instead of a box like in B-Scope. This allows one to far more accurately gauge the actual target heading relative to your aircraft in a more accurate top-down view. | The PPI scope is a more accurate representation of what your radar is seeing. It displays the radar in a cone like shape instead of a box like in B-Scope. This allows one to far more accurately gauge the actual target heading relative to your aircraft in a more accurate top-down view. | ||
| − | * | + | * |
| − | + | ===B Scope=== | |
| − | |||
| − | === B Scope === | ||
[[File:M2K BScope.jpg|frameless|465x465px|none]] | [[File:M2K BScope.jpg|frameless|465x465px|none]] | ||
The B-scope is your classic western radar scope. With the bottom of the radar representing your aircraft. | The B-scope is your classic western radar scope. With the bottom of the radar representing your aircraft. | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | === Radar modes: === | + | ===Radar modes:=== |
| − | ==== HFR - High PRF ==== | + | ====HFR - High PRF==== |
| − | * Used for long range detection, at the cost of detection range of flanking or retreating targets and a much larger notch. However this mode has the fewest limitations of the remaining two and should be the mode you use the most. | + | *Used for long range detection, at the cost of detection range of flanking or retreating targets and a much larger notch. However this mode has the fewest limitations of the remaining two and should be the mode you use the most. |
| − | ==== ENT - Interleaved ==== | + | ====ENT - Interleaved==== |
| − | * Alternates between high and low PRF this allows the radar to have the advantages of both. It has moderate detection ranges of fighter sized targets at around 45NMi however you can not guide the super 530D in this mode. | + | *Alternates between high and low PRF this allows the radar to have the advantages of both. It has moderate detection ranges of fighter sized targets at around 45NMi however you can not guide the super 530D in this mode. |
| − | ==== BFR - Low PRF ==== | + | ====BFR - Low PRF==== |
| − | * Very poor long range detection and no look down capability. The lack of a Doppler filter severely limits this mode, hoever it has no notch speed so is a great asset for engaging targets at higher altitude. | + | *Very poor long range detection and no look down capability. The lack of a Doppler filter severely limits this mode, hoever it has no notch speed so is a great asset for engaging targets at higher altitude. |
| − | |||
---- | ---- | ||
===Target Symbology=== | ===Target Symbology=== | ||
| − | ==== IFF symbology ==== | + | === STT/TWS === |
| − | <br /> | + | |
| + | |||
| + | Note pressing the () button once will put the radar into TWS, in order to go into STT you must press () a second time while hovering over the target. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====IFF symbology==== | ||
| + | The IFF on the Mirage works by scanning the entire radar volume once the command has been received and then overlaying positive or negative IFF results over tracked targets.<br /> | ||
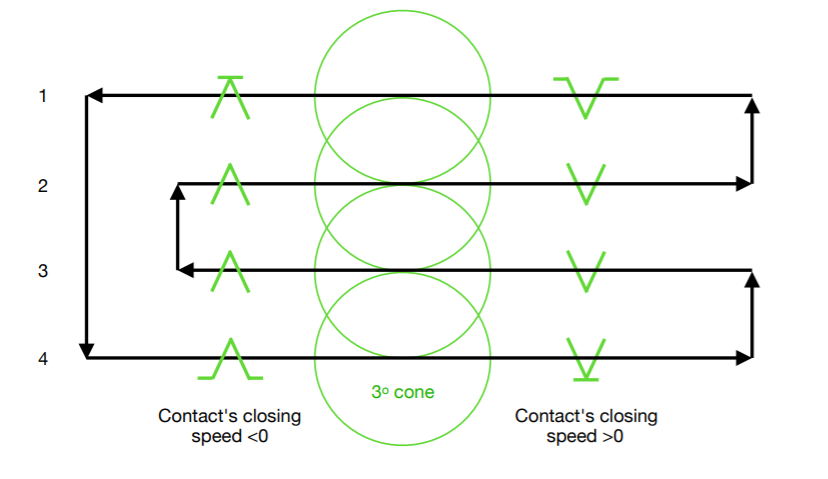
| − | === Elevation symbology === | + | ===Elevation symbology=== |
Additionally the radar will give you an indication if the target is near the extreme edges of your scan pattern. This is very useful especially if a target is not currently near your radar cursor you can quickly see if you need to depress or elevate the radar to keep the contact on the screen. | Additionally the radar will give you an indication if the target is near the extreme edges of your scan pattern. This is very useful especially if a target is not currently near your radar cursor you can quickly see if you need to depress or elevate the radar to keep the contact on the screen. | ||
| − | ==== During 4 Bar scan ==== | + | ====During 4 Bar scan==== |
[[File:M2kbar1.png|borderless|none]] | [[File:M2kbar1.png|borderless|none]] | ||
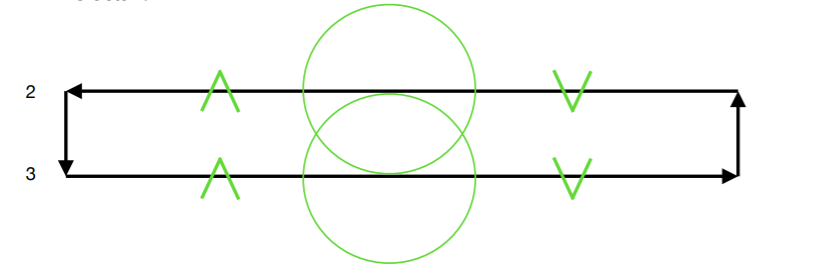
| − | ==== During 2 Bar scan ==== | + | ====During 2 Bar scan==== |
[[File:M2kbar2.png|borderless|none]] | [[File:M2kbar2.png|borderless|none]] | ||
| − | ==== During 1 Bar scan ==== | + | ====During 1 Bar scan==== |
[[File:M2kbar3.png|borderless|none]] | [[File:M2kbar3.png|borderless|none]] | ||
| − | + | ==HUD== | |
| − | |||
| − | == HUD == | ||
Revision as of 09:14, 11 February 2020
Contents
DCS M-2000C A/A introductory Guide
Introduction
The Mirage-2000C is a light delta wing interceptor built in France. It has a very limited A/A loadout with only 2x R550 Magic II short range IR missiles and 2x Super 530D medium range SARH missiles. The Mirage in terms of systems is very simple and is in general an easy aircraft to learn and operate. This makes it a great first fighter. Even though completely outmatched against western contemporaries such as the F15C and F14A/B in BVR combat this jet at the short to medium ranges can be lethal. In particular against older Russian aircraft such as the MIG-23 this aircraft can be downright lethal.
- Weapons
- Super 530D
- R550 Magic II
Weapons
Super 530D
The super 530D is a medium range high speed SARH missile. Capable of M5.0, the D model is a significant improvement over previous models with higher speed and better range. The biggest limitation of the missile is both its lifetime and CCM. Both are quite low with 45 seconds for the the former and worse CCM than the AIM-7M for the latter.
R550 Magic II
Controls
Pilot Stick
Pilot Throttle
Radar Page (RWS):
The radar is the heart of the offensive systems in the mirage. The radar scope is the screen situated just below the hud and is dedicated to the radar. The radar has several useful features that make it quite good at helping the pilot better understand the air picture without the assistance of a datalink which the mirage lacks. However the small size of the radar limits its long range detection capabilities especially when compared to other fighters in DCS.
PPI Scope
The PPI scope is a more accurate representation of what your radar is seeing. It displays the radar in a cone like shape instead of a box like in B-Scope. This allows one to far more accurately gauge the actual target heading relative to your aircraft in a more accurate top-down view.
B Scope
The B-scope is your classic western radar scope. With the bottom of the radar representing your aircraft.
Radar modes:
HFR - High PRF
- Used for long range detection, at the cost of detection range of flanking or retreating targets and a much larger notch. However this mode has the fewest limitations of the remaining two and should be the mode you use the most.
ENT - Interleaved
- Alternates between high and low PRF this allows the radar to have the advantages of both. It has moderate detection ranges of fighter sized targets at around 45NMi however you can not guide the super 530D in this mode.
BFR - Low PRF
- Very poor long range detection and no look down capability. The lack of a Doppler filter severely limits this mode, hoever it has no notch speed so is a great asset for engaging targets at higher altitude.
Target Symbology
STT/TWS
Note pressing the () button once will put the radar into TWS, in order to go into STT you must press () a second time while hovering over the target.
IFF symbology
The IFF on the Mirage works by scanning the entire radar volume once the command has been received and then overlaying positive or negative IFF results over tracked targets.
Elevation symbology
Additionally the radar will give you an indication if the target is near the extreme edges of your scan pattern. This is very useful especially if a target is not currently near your radar cursor you can quickly see if you need to depress or elevate the radar to keep the contact on the screen.
During 4 Bar scan
During 2 Bar scan
During 1 Bar scan
HUD
ACM Modes
Setup: