Difference between revisions of "Formation flying"
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
'''Fighting Wing ''' | '''Fighting Wing ''' | ||
| − | This formation, flown as a two-ship, gives the | + | This formation, flown as a two-ship, gives the |
| − | + | wingman a maneuvering | |
| − | + | cone from 30º to 70º aft of line abreast and lateral spacing | |
| − | + | between 500' to 3000' (Figure 3.7). | |
| − | + | Number two maneuvers off lead with cutoff as | |
| − | It is essentially the same as a Wedge (only closer) but with the freedom to move from side to side. | + | necessary to maintain position. |
| + | |||
| + | This formation is employed in situations where maximum | ||
| + | |||
| + | maneuvering potential is desired. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The wingman is free to switch sides at any point in the flight to aid in | ||
| + | |||
| + | maneuvering and providing coverage for flight lead. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is essentially the same as a Wedge (only closer) | ||
| + | |||
| + | but with the freedom to move from side to side. | ||
'''Line Abreast or Spread''' | '''Line Abreast or Spread''' | ||
| − | A Line Abreast (LAB) or Spread formation places the element lead and his wingman alongside of each other separated by typically 1nm. LAB formations can be difficult to fly since it requires the pilots to keep shifting their view to the side occasionally to ensure they are maintaining position. A stable flight lead flying a constant speed and heading make this easier. | + | A Line Abreast (LAB) or Spread formation places the element lead |
| + | |||
| + | and his wingman alongside of each other separated by typically 1nm. | ||
| + | |||
| + | LAB formations can be difficult to fly since it requires the pilots | ||
| + | |||
| + | to keep shifting their view to the side occasionally to ensure they are | ||
| + | |||
| + | maintaining position. A stable flight lead flying a constant speed and | ||
| + | |||
| + | heading make this easier. | ||
'''Trail''' | '''Trail''' | ||
| − | As the name implies, a Trail formation is simply the wingman following directly behind his flight lead at a specific distance; typically 1nm. The key thing to remember when maneuvering in this formation is that the wingman must delay his turns slightly in order to remain in position; the wingman needs to fly to the spot where lead began his turn before turning. | + | As the name implies, a Trail formation is simply the wingman |
| + | |||
| + | following directly behind his flight lead at a specific distance; typically 1nm. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The key thing to remember when maneuvering in this | ||
| + | |||
| + | formation is that the wingman must delay his turns slightly | ||
| + | |||
| + | in order to remain in position; the wingman needs to fly to | ||
| + | |||
| + | the spot where lead began his turn before turning. | ||
'''Route & Loose Route''' | '''Route & Loose Route''' | ||
| − | A route formation is flown to enhance clearing and | + | A route formation is flown to enhance clearing and |
| − | Loose Route simply spreads the formation out a bit; 4 ship widths instead of two. This make it even easier to be “heads down” in the pit checking radios, weapons, etc. | + | visual lookout, increase flight maneuverability, and ease the |
| + | |||
| + | completion of inflight checks, radio changes, and other cockpit tasks. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Route is flown from two-ship widths of spacing out to | ||
| + | |||
| + | approximately 500 feet. Fly no farther aft than the extended fingertip line, | ||
| + | |||
| + | no farther forward than line abreast, and, when wings level, maintain a level stack. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Loose Route simply spreads the formation out a bit; 4 ship widths instead of two. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This make it even easier to be “heads down” in the pit checking radios, weapons, etc. | ||
'''Finger-4''' | '''Finger-4''' | ||
| − | As the name implies, this is the 4-ship version of fingertip formation and looks similar to the position of your fingertips on your right hand with #3 flying a mirror of #2 (on the right side) and his wingman in fingertip off of him. Need a picture? Look at your right hand. | + | As the name implies, this is the 4-ship version of fingertip formation |
| + | |||
| + | and looks similar to the position of your fingertips on your right | ||
| + | |||
| + | hand with #3 flying a mirror of #2 (on the right side) and his wingman | ||
| + | |||
| + | in fingertip off of him. Need a picture? Look at your right hand. | ||
'''Fluid -4''' | '''Fluid -4''' | ||
| − | This is essentially two Fighting Wing formations in a spread / LAB formation. When performing tac turns from this formation, #1 and #3 perform the turns as though they were a 2-ship element and their respective wingmen tag along switching sides on their respective leads as needed | + | This is essentially two Fighting Wing formations in a spread / LAB formation. |
| + | |||
| + | When performing tac turns from this formation, #1 and #3 perform | ||
| + | |||
| + | the turns as though they were a 2-ship element and their respective | ||
| + | |||
| + | wingmen tag along switching sides on their respective leads as needed | ||
'''Box or Offset Box''' | '''Box or Offset Box''' | ||
| − | A Box formation is a pair of LAB formations with the second element in trail behind lead element. More common is the Offset Box which simply slides the trailing element to the side (#3 flies between #1 and #2). Note in both the Box and Offset Box the #2 wingman is on the right side of flight lead. Flight leads may call or brief a “Box Left” meaning #2 (and therefore #4 as well) remain on the on the left side. | + | A Box formation is a pair of LAB formations with the second element |
| + | |||
| + | in trail behind lead element. More common is the Offset Box which | ||
| + | |||
| + | simply slides the trailing element to the side (#3 flies between #1 and #2). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note in both the Box and Offset Box the #2 wingman is on the right side of flight lead. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Flight leads may call or brief a “Box Left” meaning #2 (and therefore #4 as well) | ||
| + | |||
| + | remain on the on the left side. | ||
[[Category:UOAF]] | [[Category:UOAF]] | ||
[[Category:UOAF: BMS Codex]] | [[Category:UOAF: BMS Codex]] | ||
[[Category:UOAF: General Basic Competencies]] | [[Category:UOAF: General Basic Competencies]] | ||
Revision as of 21:59, 6 March 2017
Basic intro info about formation flying. What it is.
Contents
Learning objectives
- =Understand Basic Tactical Formation Concepts/Theory=
- Execute Basic Tactical Formation Flying
- Wingman Responsibilities
Learning files
- Learning TE =available in a 2-part flight with white board=
- Video
- ACMI>>>>>>>working on this now
More Info
More detail here, if required. Embedded images and video links.
Formations
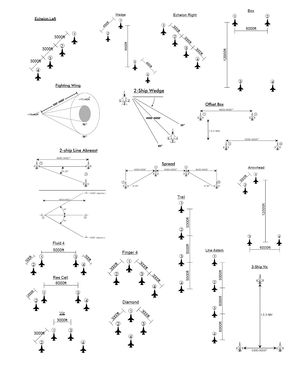
The most common flight formations we use are Wedge or Finger Four, since these are the easiest to maintain as the wingman. Wedge is basically two fighting wings separated by 3-5 miles.
Remember to not fly too close. Flying wingtip to wingtip severely limits your ability to manoeuvre and restricts your ability to check your six visually. Stay within visual range and far enough to the side that your leader can see you, but far enough away that you can see him if he changes altitude and do evasive manoeuvres without risking a collision.
Being a wingman
A flight consists of four aircraft, or ships. The flight leader is #1, the element leader is #3. Their wingmen are #2 and #4, respectively.
In general, it's the flight and element leader's jobs to do the actual tactics parts of the mission. The wingmen are there to be an extension of the element leader's senses and firepower. Your primary tasks as a wingman is to follow your element leader, watch his back and the surrounding area visually while the lead is dealing with radar/sensors, and engage targets as directed by the element leader. Navigation and looking at the radar are not your prime concerns. You have to keep an eye on it, but your head should primarily be outside the cockpit, looking around and making sure you're with your lead in case he manouvres around. If your element leader deviates from the flight plan (especially by suddenly going very fast or very slow), you follow him. Tell him about it to make sure he hasn't missed a turn or hasn't checked his speed, but stay on him no matter what.
When attacking a target, the flight or element leader will call a group and then "SORT". This means to pick out the target in the enemy formation corresponding to your place in your formation. If you're an element attacking an enemy two-ship group, the wingman should take the enemy wingman, who's usually trailing behind. If you're in a wedge, you will be roughly lined up from left to right as 2-1-3-4. If you're attacking an enemy four-ship, 2 will take the enemy to the far left (from your perspective), 1 takes the one to right of that one, etc. If the datalink is in use, you will see which enemies your wingmates are engaging, and you might be specifically assigned a target by the lead which will show up on your radar.
Flight tactics
A flight expecting to engage enemy aircraft will often start out in a wedge formation, i.e. one flight following the other at between 3-5 miles. When the first element gets a contact it will fire missiles and turn away, towards the second element. The second element flies on into their engagement range and does the same. The first element will then have turned back and are inbound to attack the targets again. This tactic is called a "grinder" and is very often used if your flight is operating on its own against enemies, and is used to slowly grind down the enemy numbers until they all die or the survivors run away.
Another, more complex, tactic that's seldom used is to fly both elements abrest with a large spacing of 3-5 miles. If an enemy group is encountered, they will most likely attempt to engage one of the elements. In that case, the defensive element can turn away, allowing the other element to attack the enemies from behind.
=Finger-Tip or Echelon=
In the F-16, a finger-tip formation can be achieved by flying along a line
of sight that has the lead pilot’s vertical stabilizer covering the opposite
wing. The pilot can also use the wingtip missile as a guide by lining it up
with the intake.
Most pilots tend to fly in a “sucked” position, meaning they are too far
back resulting in the lead pilot being unable to see his wingman. It is
better to be spread further and maintain the same line of sight (tail
covering opposite wing) than be in a sucked position.
Echelon formations (left or right) are the same as Finger-tip when
flying as a 2-ship. When more than 2, all ships are on the same
side of lead so that #3 flies finger-tip off of #2 and so on.
Wedge
Wedge is defined as the wingman positioned from 30º to
60º aft of the leader's 3/9 line, 4000' to 6,000' back. The
advantages of wedge are that the leader is well protected
in the 6 o'clock area and is free to maneuver aggressively.
The wingman may switch sides as required during turns.
He may also switch sides as required to avoid terrain,
obstacles or weather but must return to the original side
unless cleared by the leader.
Fighting Wing
This formation, flown as a two-ship, gives the
wingman a maneuvering
cone from 30º to 70º aft of line abreast and lateral spacing
between 500' to 3000' (Figure 3.7).
Number two maneuvers off lead with cutoff as
necessary to maintain position.
This formation is employed in situations where maximum
maneuvering potential is desired.
The wingman is free to switch sides at any point in the flight to aid in
maneuvering and providing coverage for flight lead.
It is essentially the same as a Wedge (only closer)
but with the freedom to move from side to side.
Line Abreast or Spread
A Line Abreast (LAB) or Spread formation places the element lead
and his wingman alongside of each other separated by typically 1nm.
LAB formations can be difficult to fly since it requires the pilots
to keep shifting their view to the side occasionally to ensure they are
maintaining position. A stable flight lead flying a constant speed and
heading make this easier.
Trail
As the name implies, a Trail formation is simply the wingman
following directly behind his flight lead at a specific distance; typically 1nm.
The key thing to remember when maneuvering in this
formation is that the wingman must delay his turns slightly
in order to remain in position; the wingman needs to fly to
the spot where lead began his turn before turning.
Route & Loose Route
A route formation is flown to enhance clearing and
visual lookout, increase flight maneuverability, and ease the
completion of inflight checks, radio changes, and other cockpit tasks.
Route is flown from two-ship widths of spacing out to
approximately 500 feet. Fly no farther aft than the extended fingertip line,
no farther forward than line abreast, and, when wings level, maintain a level stack.
Loose Route simply spreads the formation out a bit; 4 ship widths instead of two.
This make it even easier to be “heads down” in the pit checking radios, weapons, etc.
Finger-4
As the name implies, this is the 4-ship version of fingertip formation
and looks similar to the position of your fingertips on your right
hand with #3 flying a mirror of #2 (on the right side) and his wingman
in fingertip off of him. Need a picture? Look at your right hand.
Fluid -4
This is essentially two Fighting Wing formations in a spread / LAB formation.
When performing tac turns from this formation, #1 and #3 perform
the turns as though they were a 2-ship element and their respective
wingmen tag along switching sides on their respective leads as needed
Box or Offset Box
A Box formation is a pair of LAB formations with the second element
in trail behind lead element. More common is the Offset Box which
simply slides the trailing element to the side (#3 flies between #1 and #2).
Note in both the Box and Offset Box the #2 wingman is on the right side of flight lead.
Flight leads may call or brief a “Box Left” meaning #2 (and therefore #4 as well)
remain on the on the left side.